
Github Actions
GitHub Actions for Android CI/CD






Published on Dec 19, 2022 by Man Ho on Android Development

First, we need to create a YAML file inside .github/workflows/workflow_name.yml
Then declare the workflow name and when it will be triggered:
name: Workflow name
on:
push:
branches:
"branch name"
pull_request:
branches:
"branch name"
...
And then we have jobs describing its steps in this workflow:
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
build is job name, and runs-on that declare the virtual machine that we use.
After that, we have steps in that build job First of all, sure, we need to checkout the latest code before doing anything:
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v2
In here:
We also need Java to build our Android app, so this is the step for setting up environment:
- name: Setup JDK environment
uses: actions/setup-java@v1
with:
java-version: 11
For this, we will use the actions/setup-java action to set up Java on the virtual machine.
This can improve the performance of the build, it will use cached dependencies instead of downloading from the internet:
- name: Gradle caching
uses: actions/cache@v2
with:
path: ~/.gradle/caches
key: $-gradle-$
restore-keys: |
$-gradle-
We run ./gradlew assembleDebug, this command will compile and generate debug builds of all flavors.
- name: Build debug APKs
run: ./gradlew assembleDebug
This is used to save sensitive information that you need to hide instead of declaring it directly in the workflow script, such as: token, API key,…
Steps to create a GitHub Actions secret:
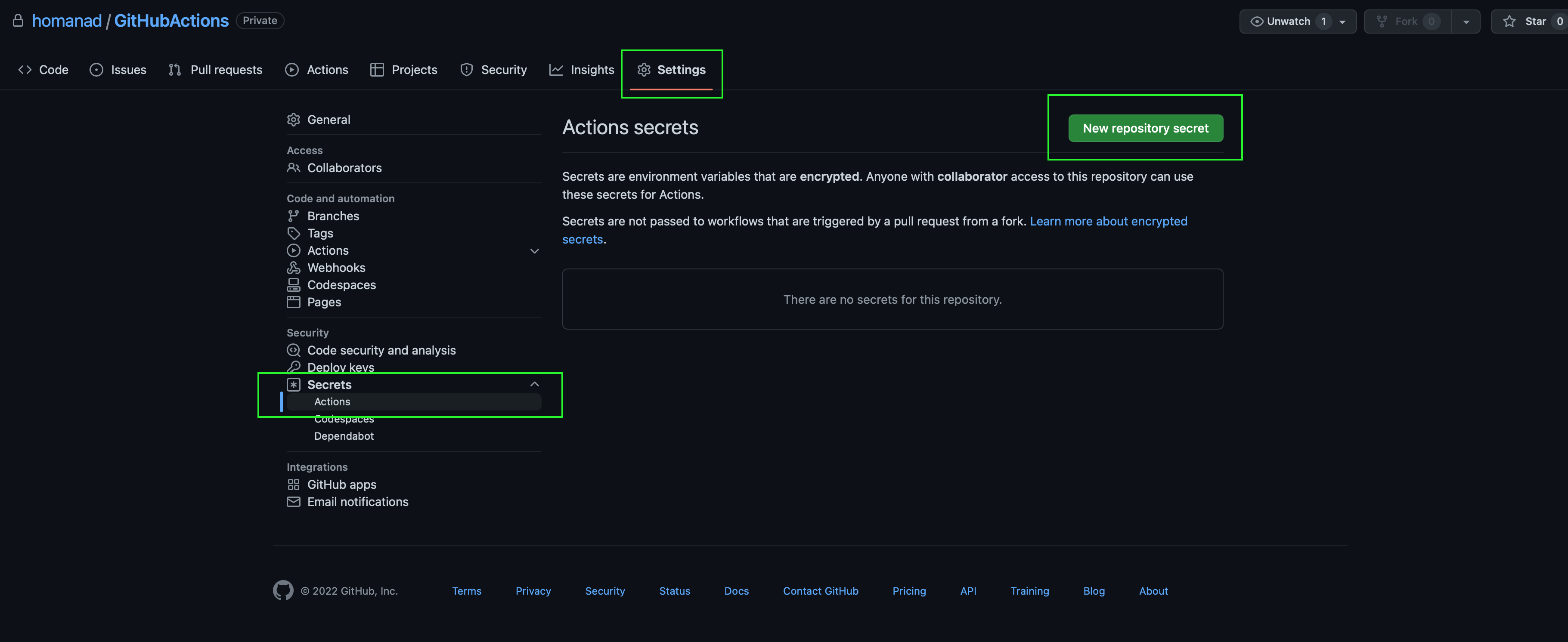
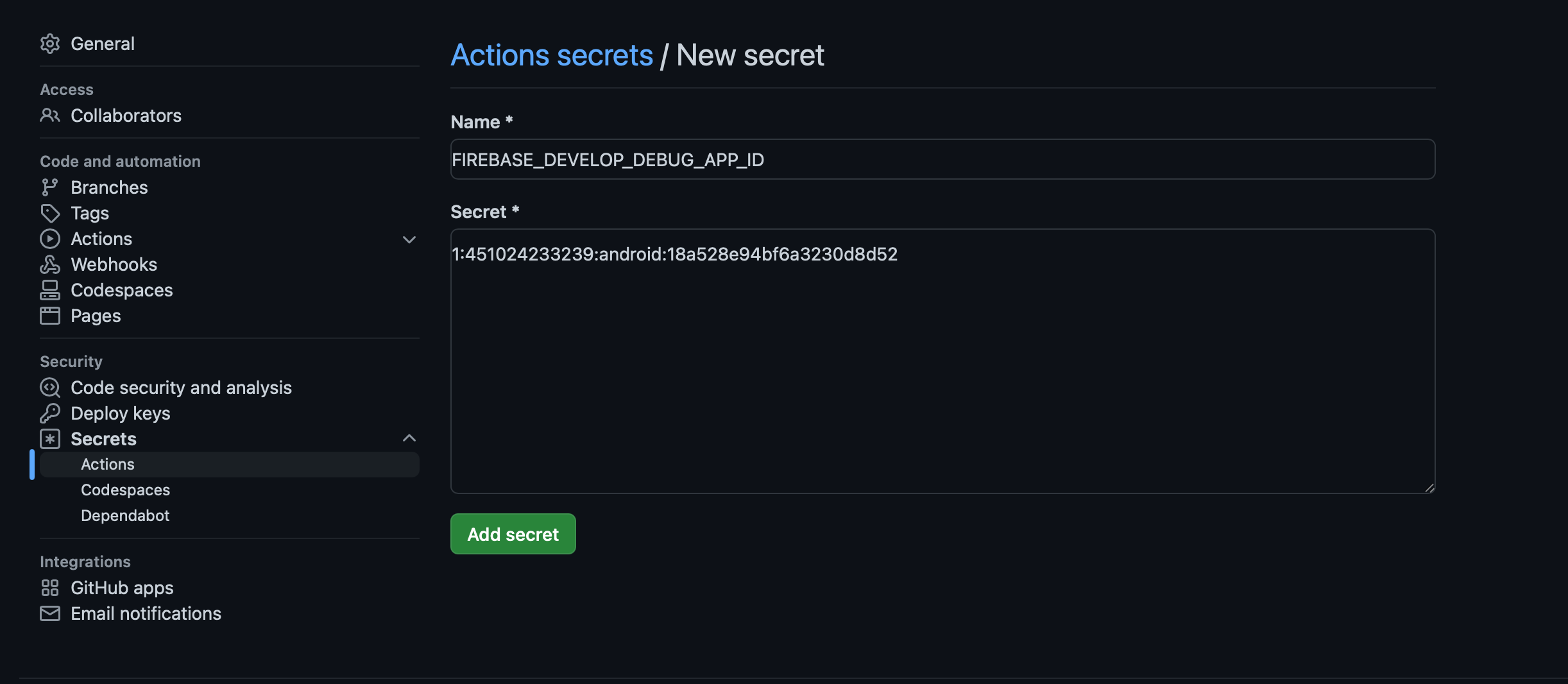
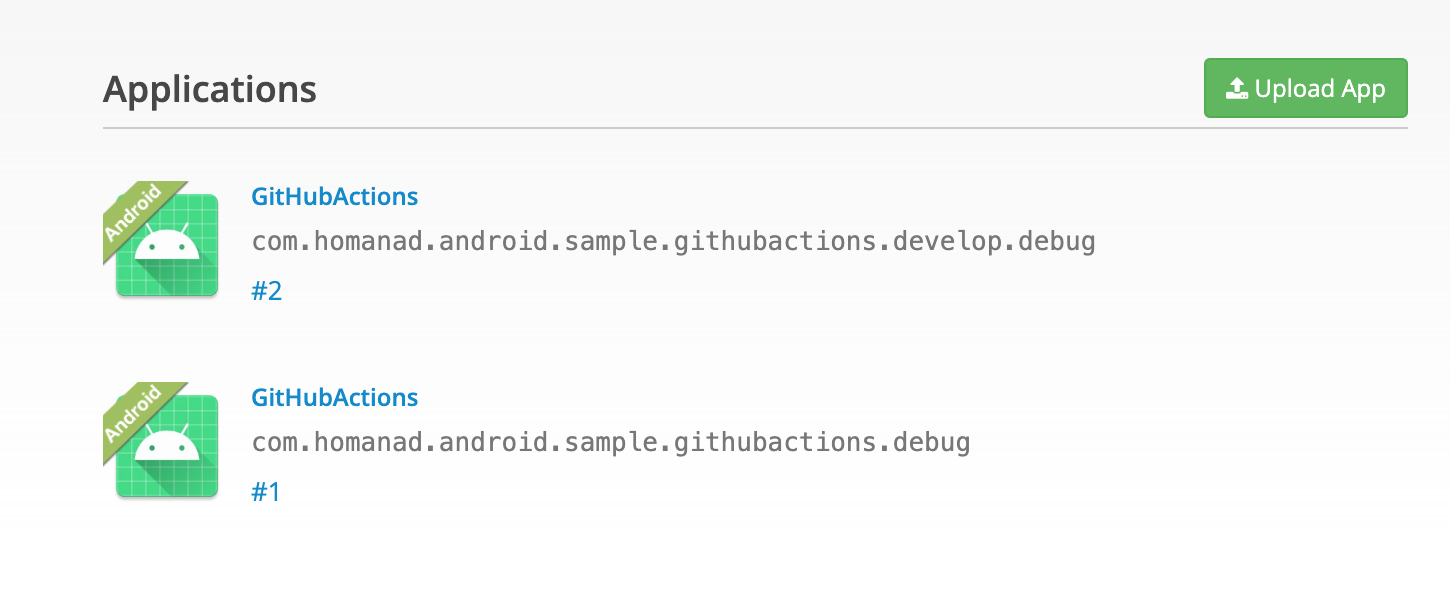
We need two secrets: Firebase App id and Firebase App distribution credential content.
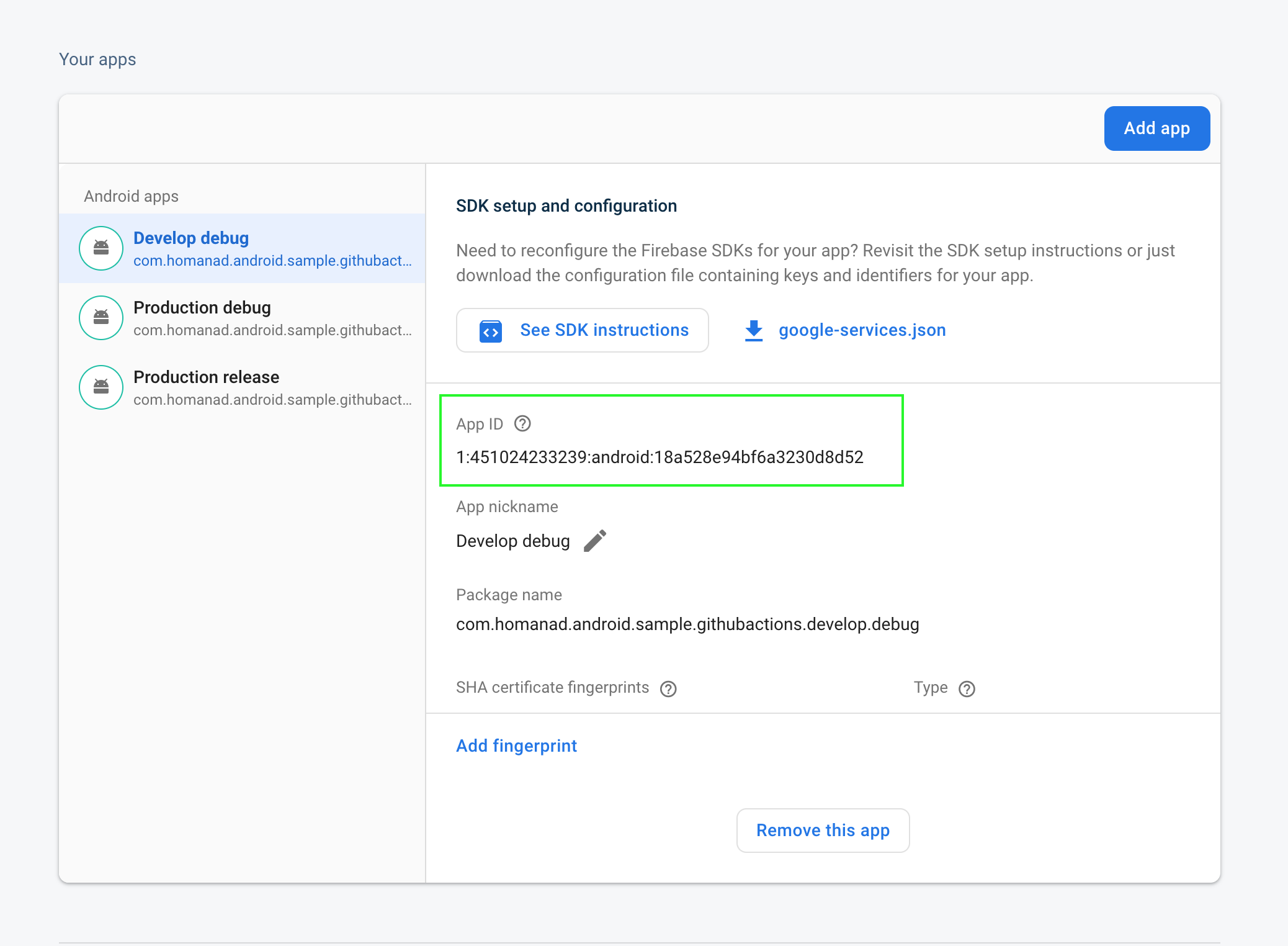
To get Firebase App id: let’s go to project settings, in applications section, select your app and you will see the App ID:
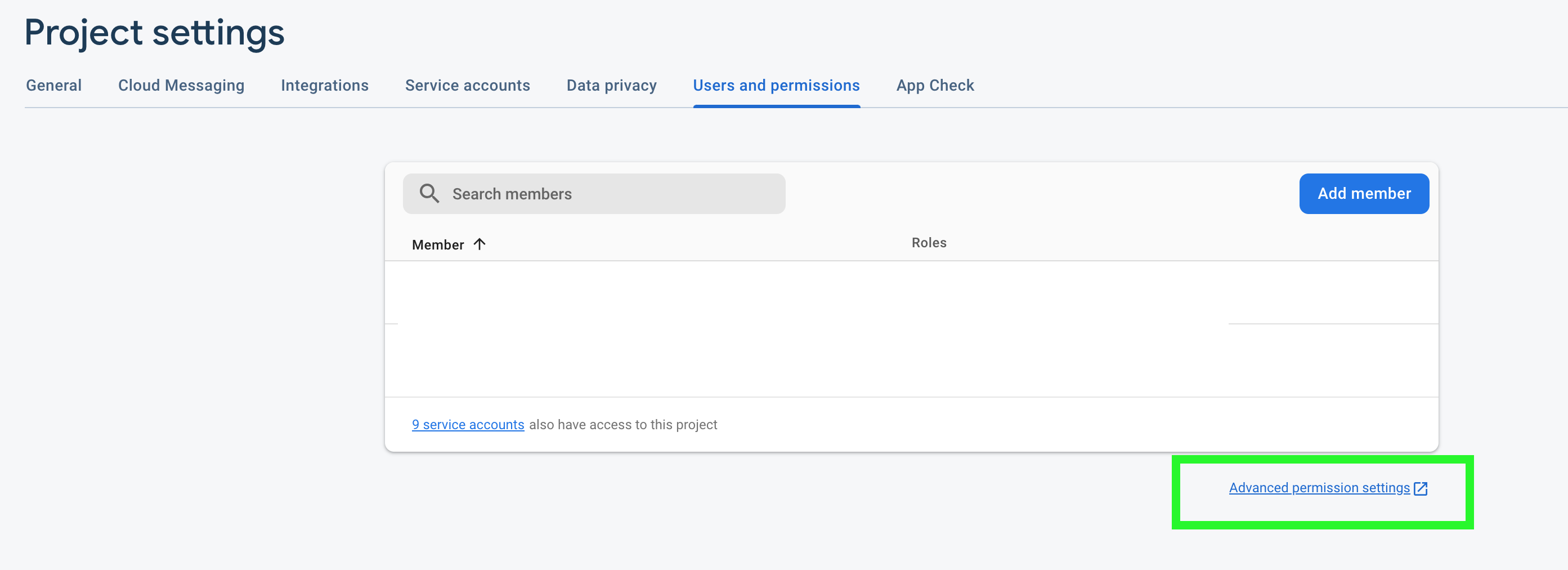
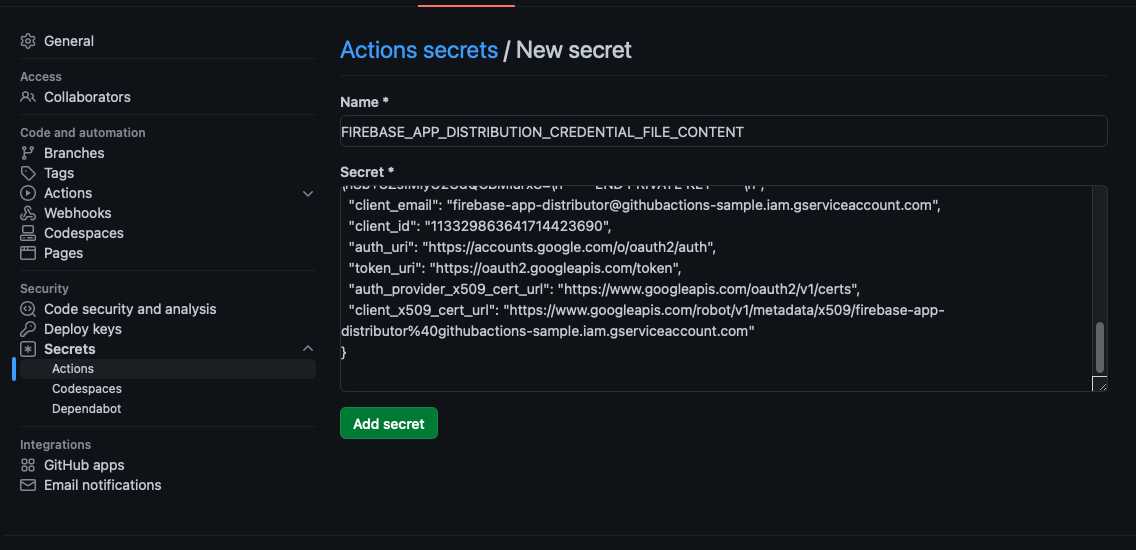
About Firebase Distribution key:
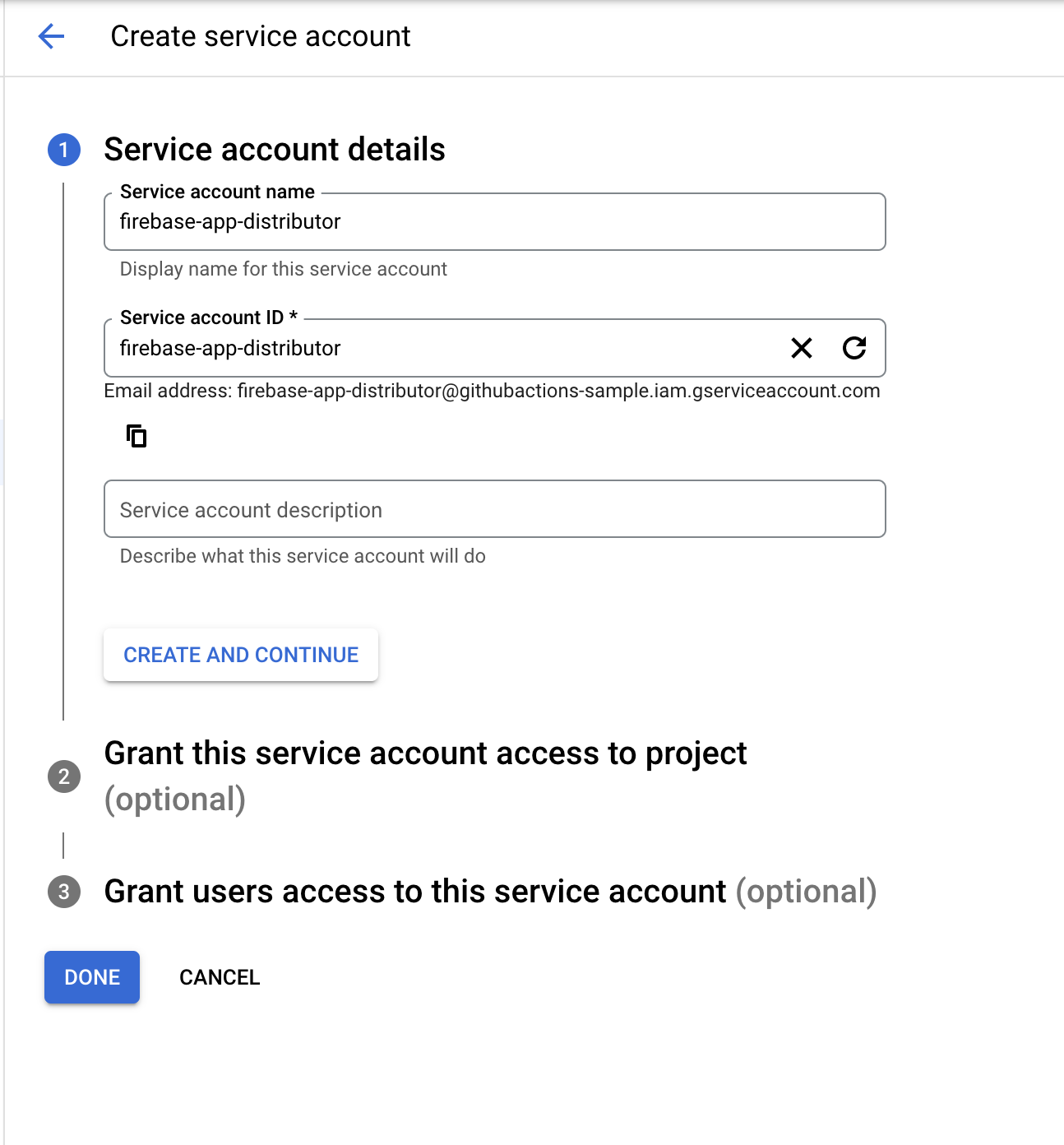
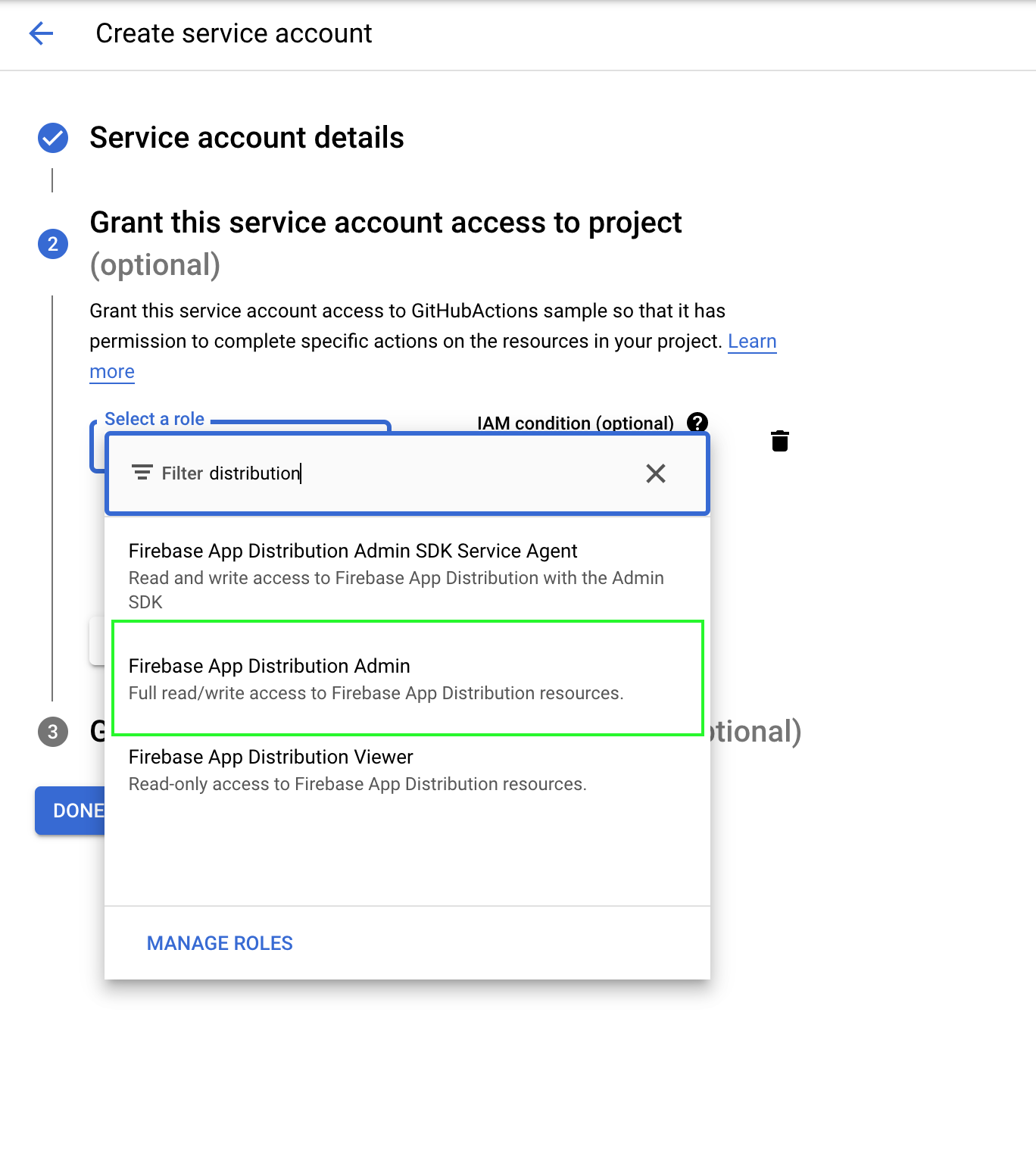
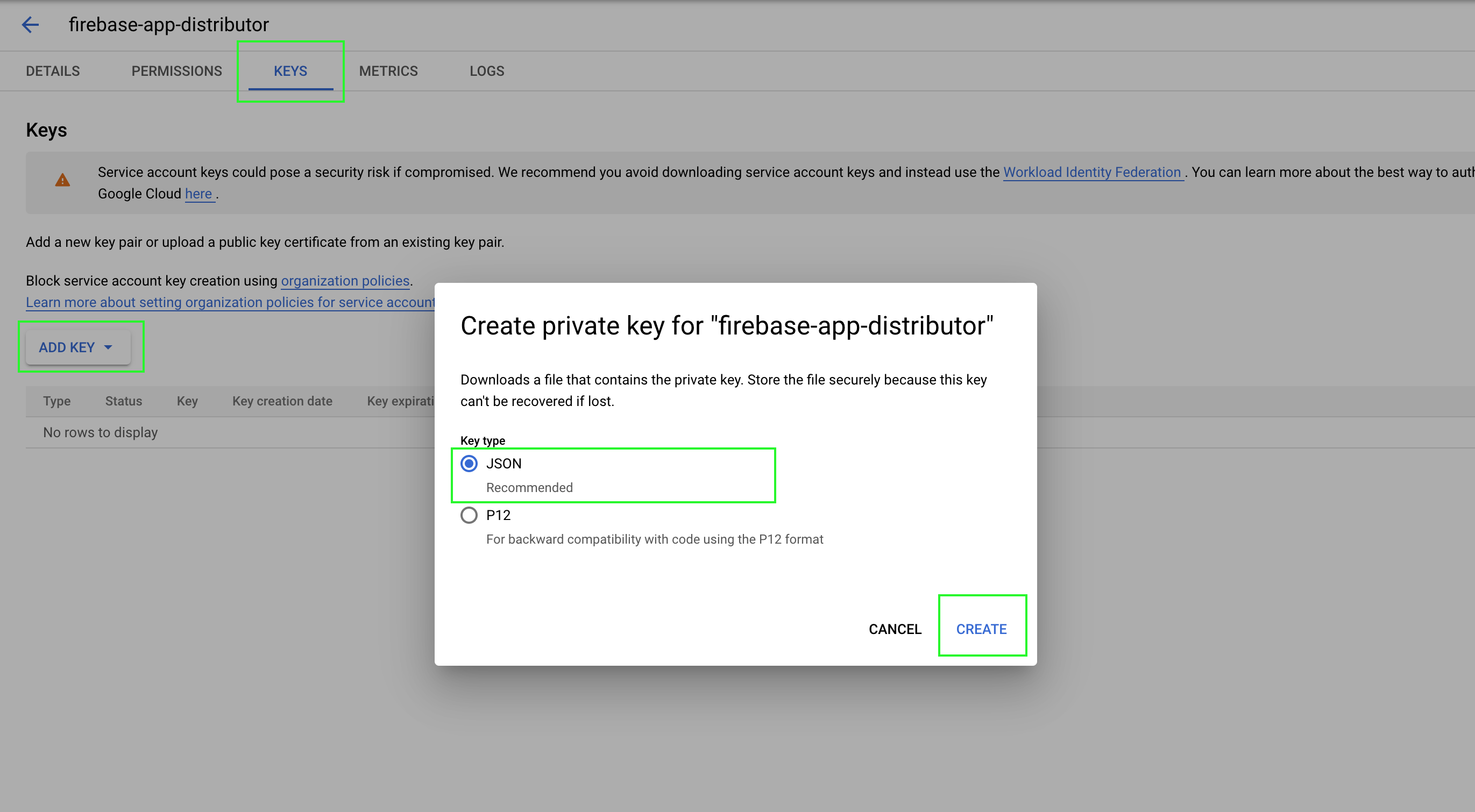
Now let’s create two GitHub secrets for Firebase App ID and Firebase App Distribution credential content:
Copy json content to create secret for firebase app distribution
Now go to Firebase and setup App Distribution
On Firebase, open Release & Monitor section and select App Distribution, click Get started, then please setup your testers and groups if needed, for me, I create a tester group with name “ testers”
Now let’s create our upload step
- name: Upload develop debug APK to Firebase App Distribution
uses: wzieba/Firebase-Distribution-Github-Action@v1
with:
appId: $
serviceCredentialsFileContent: $
groups: testers
releaseNotes: $
file: app/build/outputs/apk/develop/debug/app-develop-debug.apk
For this, we use wzieba/Firebase-Distribution-Github-Action action
Likewise, I will also create a step to upload production debug APK
- name: Upload production debug APK to Firebase App Distribution
uses: wzieba/Firebase-Distribution-Github-Action@v1
with:
appId: $
serviceCredentialsFileContent: $
groups: testers
releaseNotes: $
file: app/build/outputs/apk/production/debug/app-production-debug.apk
DeployGate is also a place that I use often in my projects because of its quickness and its easy to use, just register for an account to be able to use it.
To be able to upload our APKs to DeployGate, we only need 2 pieces of information: username( owner) name) and API Key, you can go to Account Settings and can see them, I will also create 2 secrets for these information. And this time I will also create step to upload production debug apk
- name: Upload develop debug APK to DeployGate
uses: jmatsu/dg-upload-app-action@v0.2
with:
app_owner_name: $
api_token: $
app_file_path: app/build/outputs/apk/develop/debug/app-develop-debug.apk
- name: Upload production debug APK to DeployGate
uses: jmatsu/dg-upload-app-action@v0.2
with:
app_owner_name: $
api_token: $
app_file_path: app/build/outputs/apk/production/debug/app-production-debug.apk
The last one, I want to upload our debug builds to workflow artifacts:
- name: Upload artifacts
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: Debug builds
path: |
app/build/outputs/apk/develop/debug/app-develop-debug.apk
app/build/outputs/apk/production/debug/app-production-debug.apk
name: Build and upload debug APK
on:
push:
branches:
"develop"
pull_request:
branches:
"develop"
types:
- closed
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v3.2.0
- name: Setup JDK environment
uses: actions/setup-java@v3.9.0
with:
distribution: 'temurin'
java-version: 11
cache: 'gradle'
- name: Gradle caching
uses: actions/cache@v3.0.11
with:
path: ~/.gradle/caches
key: $-gradle-$
restore-keys: |
$-gradle
- name: Build debug APKs
run: ./gradlew assembleDebug
- name: Upload develop debug APK to Firebase App Distribution
uses: wzieba/Firebase-Distribution-Github-Action@v1.4.0
with:
appId: $
serviceCredentialsFileContent: $
groups: testers
releaseNotes: $
file: app/build/outputs/apk/develop/debug/app-develop-debug.apk
- name: Upload production debug APK to Firebase App Distribution
uses: wzieba/Firebase-Distribution-Github-Action@v1.4.0
with:
appId: $
serviceCredentialsFileContent: $
groups: testers
releaseNotes: $
file: app/build/outputs/apk/production/debug/app-production-debug.apk
- name: Upload develop debug APK to DeployGate
uses: jmatsu/dg-upload-app-action@v0.2.2
with:
app_owner_name: $
api_token: $
app_file_path: app/build/outputs/apk/develop/debug/app-develop-debug.apk
- name: Upload production debug APK to DeployGate
uses: jmatsu/dg-upload-app-action@v0.2.2
with:
app_owner_name: $
api_token: $
app_file_path: app/build/outputs/apk/production/debug/app-production-debug.apk
- name: Upload artifacts
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: Debug builds
path: |
app/build/outputs/apk/develop/debug/app-develop-debug.apk
app/build/outputs/apk/production/debug/app-production-debug.apk
Since I configured this workflow only start when a commit is pushed or a pull_request is merged in develop branch, so I’ll create a develop branch and push current code.
This is workflow running:
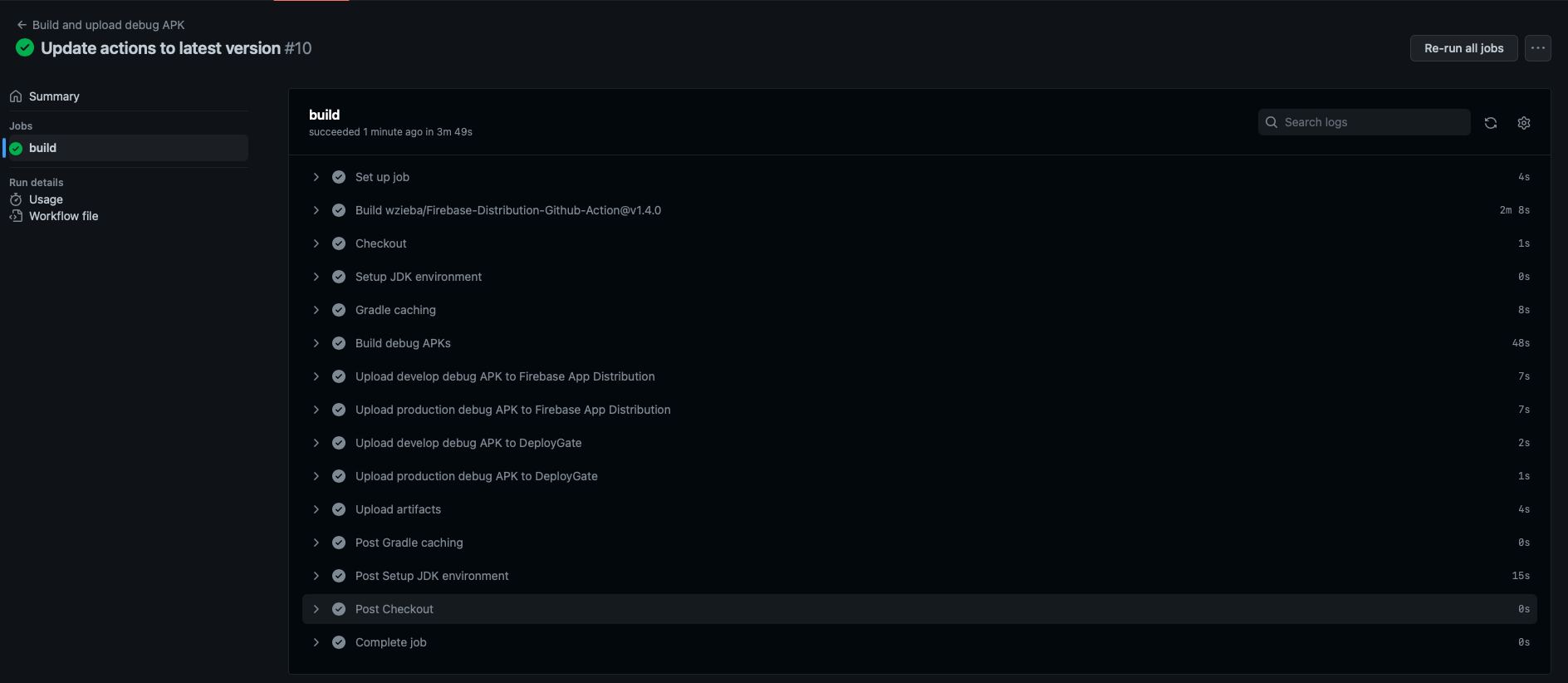
And this is our artifacts

Both develop & production debug APKs are uploaded successfully to Firebase App Distribution:
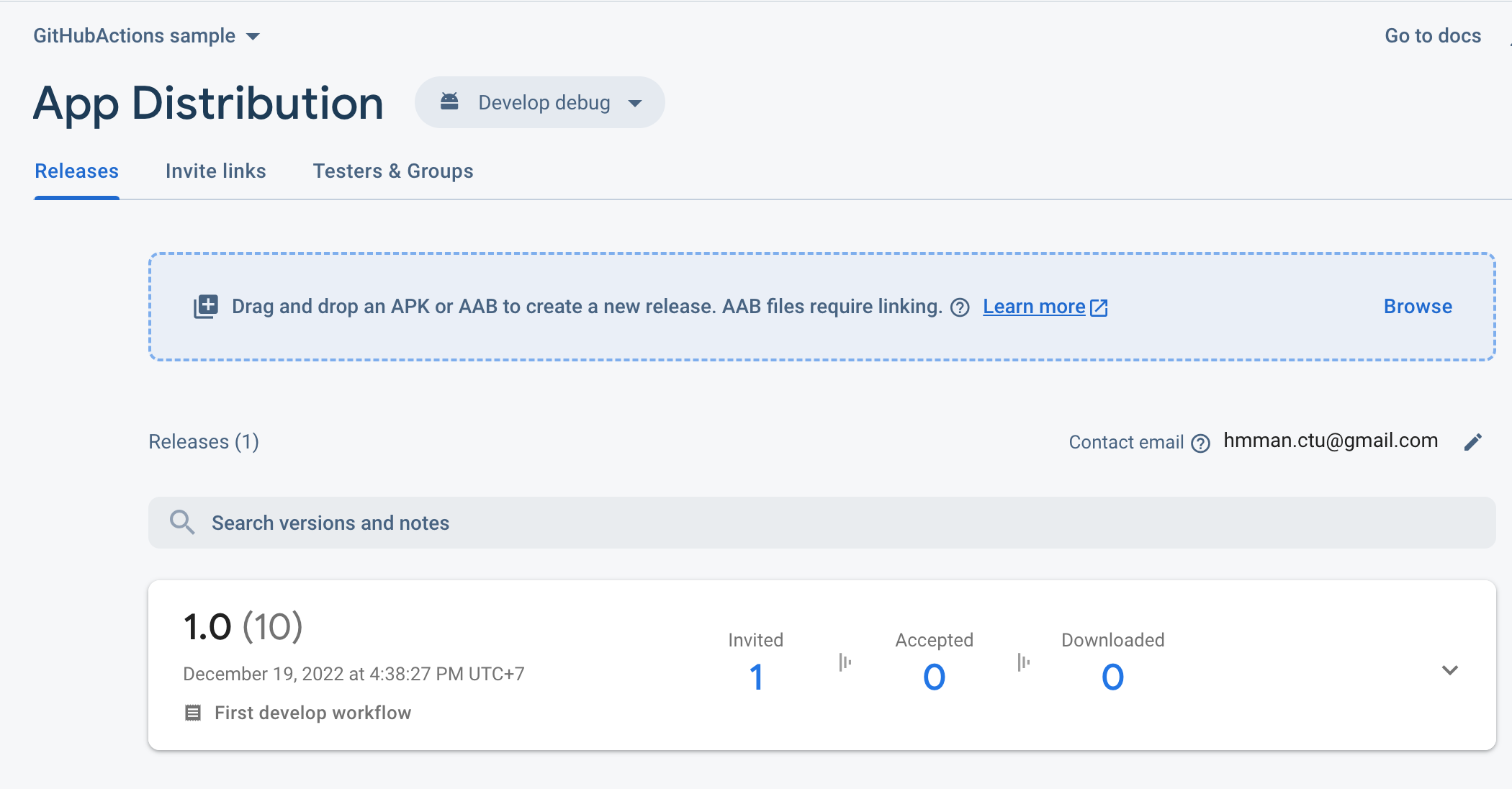
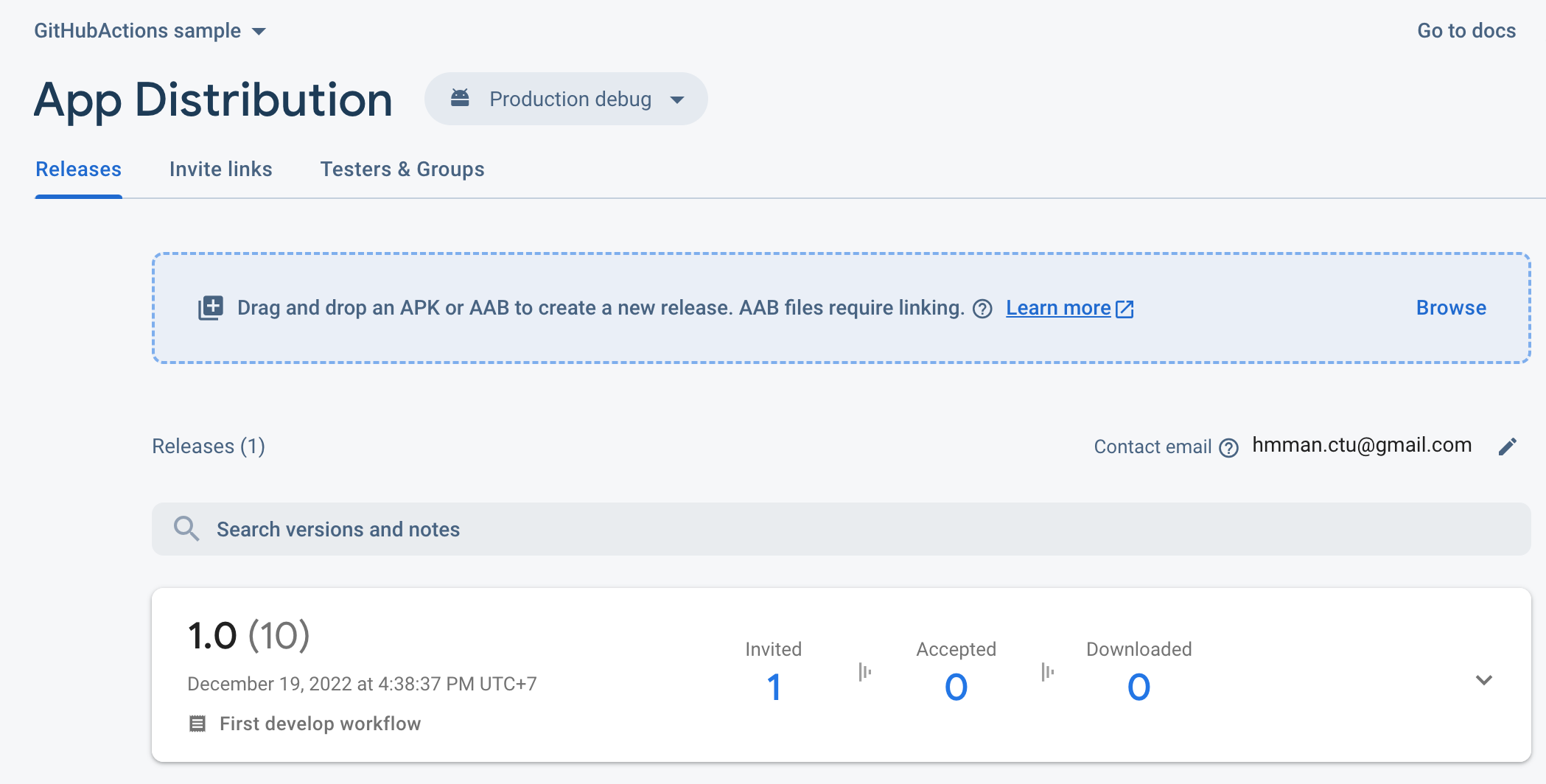
Also, both develop & production debug APKs are uploaded successfully to Firebase App Distribution:
For production release, we have many jobs that need to do, such as: upload to Google Play production/internal test/open test, create a git tag and a release,… So many thing!
But in this example, we just go though create a git tag and make a release on GitHub, let’s get started!
For this workflow, I want it to run when a pull request to “master” branch is merged. So I will create another workflow file master_workflow.yml
on:
pull_request:
branches:
"master"
types:
- closed
Here is the config so that this workflow is triggered when a pull request is merged. Next we there will still be Checkout, Setup JDK environment, Gradle caching steps, so I won’t describe it here.
After setting up the environment, we will start creating a unsigned production release build.
- name: Create release build
run: ./gradlew assembleProductionRelease
In order for a release apk to be installable on an Android device, the APK needs to be signed, in preparation for For this step, you first need to have the keystore file of this project. For this example I will create a new keystore.
Next we need to save this keystore as a Github secret, because github secret only accepts string, so we have to get the base64 encoded string of the keystore, follow this tutorial to get it: https://stefma.medium.com/how-to-store-a-android-keystore-safely-on-github-actions-f0cef9413784
Of course, we will also store keystore password, key alias and alias password on the github secret.
In total we will have 4 new secrets as follows:
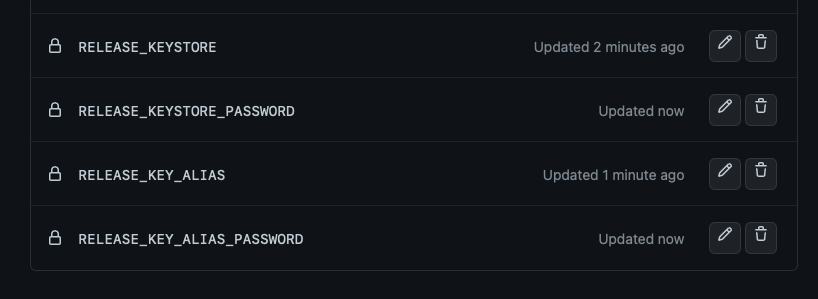
and here is the script to sign release APK:
- name: Sign release APK
uses: r0adkll/sign-android-release@v1.0.4
with:
releaseDirectory: app/build/outputs/apk/production/release
alias: $
signingKeyBase64: $
keyStorePassword: $
keyPassword: $
Here I use r0adkll/sign-android-release action, provide the directory path containing the release APK and keystore information to sign APK.
Then I will also upload the artifact like the develop workflow:
- name: Upload artifact
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: Release artifact
path: app/build/outputs/apk/production/release/*.apk
To create a release, I want to get information about the version code and version name of the app to set name for your release. So I will write 2 more gradle tasks inside app/build.gradle:
task printVersionName {
println android.defaultConfig.versionName
}
Then I used the gradew command to run the task I just created:
- name: Retrieve version name
run: |
echo "::set-output name=VERSION_NAME::$($/gradlew -q printVersionName)"
id: android_version_name
Then save the above information to GITHUB_ENV for later use:
- name: Get version name
run: |
echo "VERSION_NAME=$" >> $GITHUB_ENV
Now it’s time to create the release:
- name: Create release
id: create_release
uses: actions/create-release@v1.1.4
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $
with:
tag_name: tags/$
release_name: $
draft: false
prerelease: false
I will save the APK path and APK name to GITHUB_ENV:
- name: Save name of our Artifact
id: set-result-artifact
run: |
ARTIFACT_PATHNAME_APK=$(ls app/build/outputs/apk/production/release/*.apk | head -n 1)
ARTIFACT_NAME_APK=$(basename $ARTIFACT_PATHNAME_APK)
echo "ARTIFACT_NAME_APK is " ${ARTIFACT_NAME_APK}
echo "ARTIFACT_PATHNAME_APK=${ARTIFACT_PATHNAME_APK}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "ARTIFACT_NAME_APK=${ARTIFACT_NAME_APK}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
Then upload release artifacts:
- name: Upload our Artifact Assets
id: upload-release-asset
uses: actions/upload-release-asset@v1.0.2
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $
with:
upload_url: $
asset_path: $
asset_name: $
asset_content_type: application/zip
name: Build and create release
on:
pull_request:
branches:
"master"
types:
- closed
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v3.2.0
- name: Setup JDK environment
uses: actions/setup-java@v3.9.0
with:
distribution: 'temurin'
java-version: 11
cache: 'gradle'
- name: Gradle caching
uses: actions/cache@v3.0.11
with:
path: ~/.gradle/caches
key: $-gradle-$
restore-keys: |
$-gradle
- name: Create release build
run: ./gradlew assembleProductionRelease
- name: Sign release APK
uses: r0adkll/sign-android-release@v1.0.4
with:
releaseDirectory: app/build/outputs/apk/production/release
alias: $
signingKeyBase64: $
keyStorePassword: $
keyPassword: $
- name: Upload artifact
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
with:
name: Release artifact
path: app/build/outputs/apk/production/release/*.apk
- name: Retrieve version name
run: |
echo "::set-output name=VERSION_NAME::$($/gradlew -q printVersionName)"
id: android_version_name
- name: Get version name
run: |
echo "VERSION_NAME=$" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Create release
id: create_release
uses: actions/create-release@v1.1.4
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $
with:
tag_name: tags/$
release_name: $
draft: false
prerelease: false
- name: Save name of our Artifact
id: set-result-artifact
run: |
ARTIFACT_PATHNAME_APK=$(ls app/build/outputs/apk/production/release/*.apk | head -n 1)
ARTIFACT_NAME_APK=$(basename $ARTIFACT_PATHNAME_APK)
echo "ARTIFACT_NAME_APK is " ${ARTIFACT_NAME_APK}
echo "ARTIFACT_PATHNAME_APK=${ARTIFACT_PATHNAME_APK}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
echo "ARTIFACT_NAME_APK=${ARTIFACT_NAME_APK}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Upload our Artifact Assets
id: upload-release-asset
uses: actions/upload-release-asset@v1.0.2
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: $
with:
upload_url: $
asset_path: $
asset_name: $
asset_content_type: application/zip
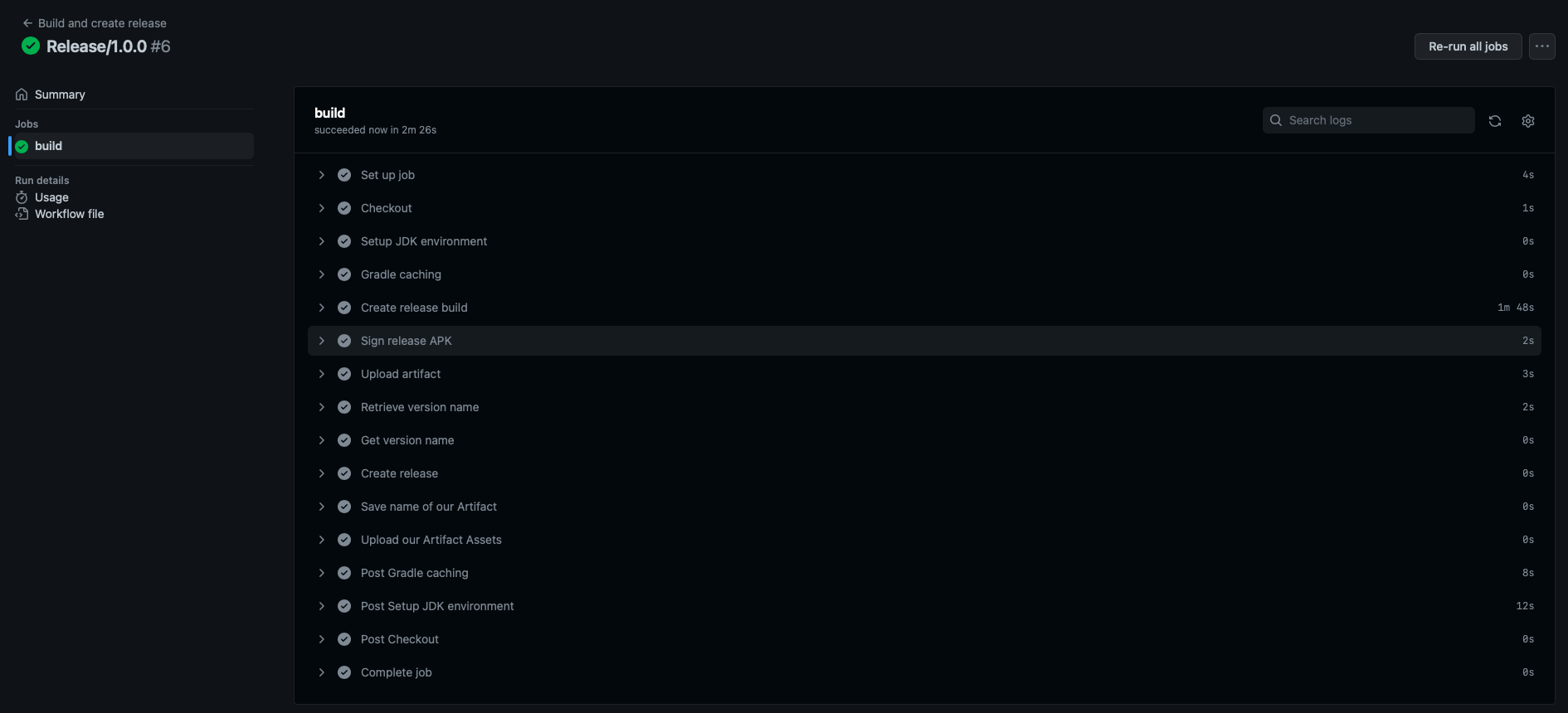
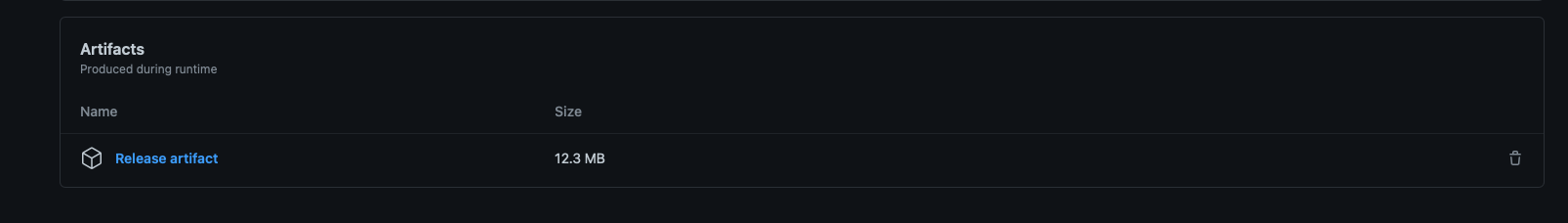
Release artifacts were uploaded:
Release 1.0.0 was created: 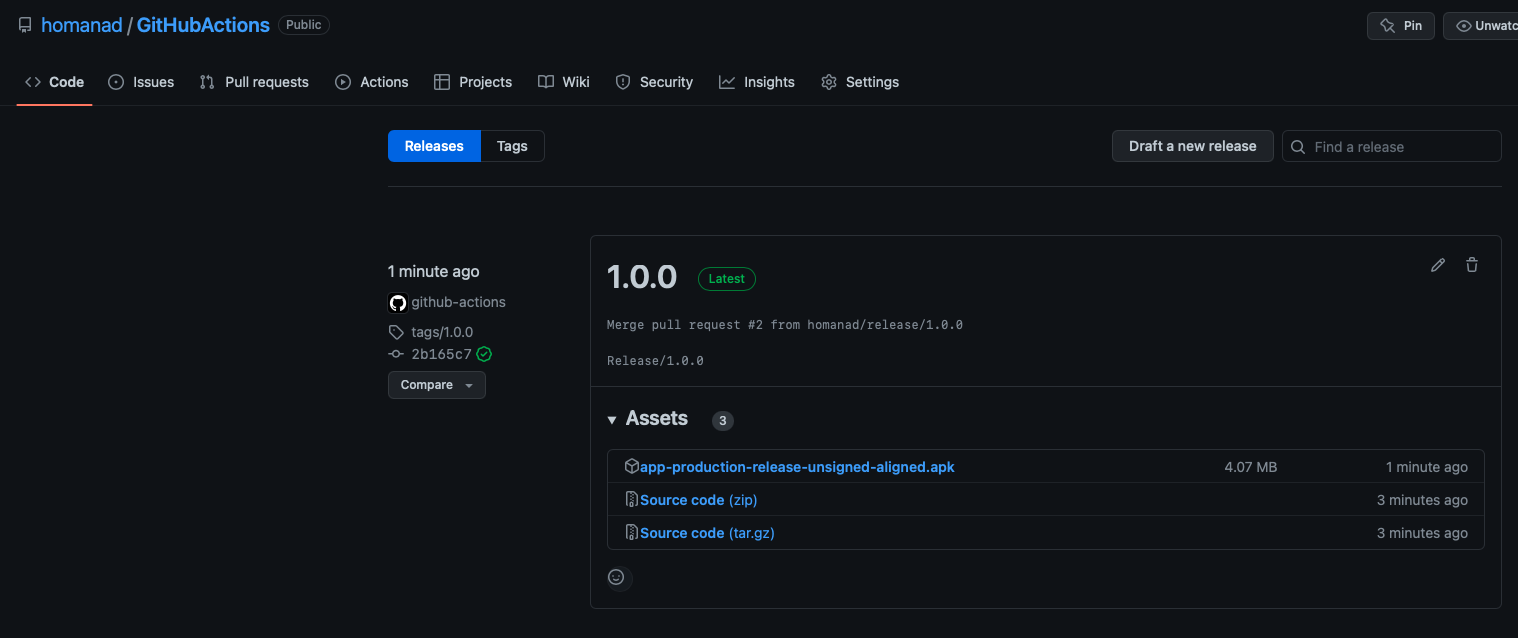
tags/1.0.0 was created: 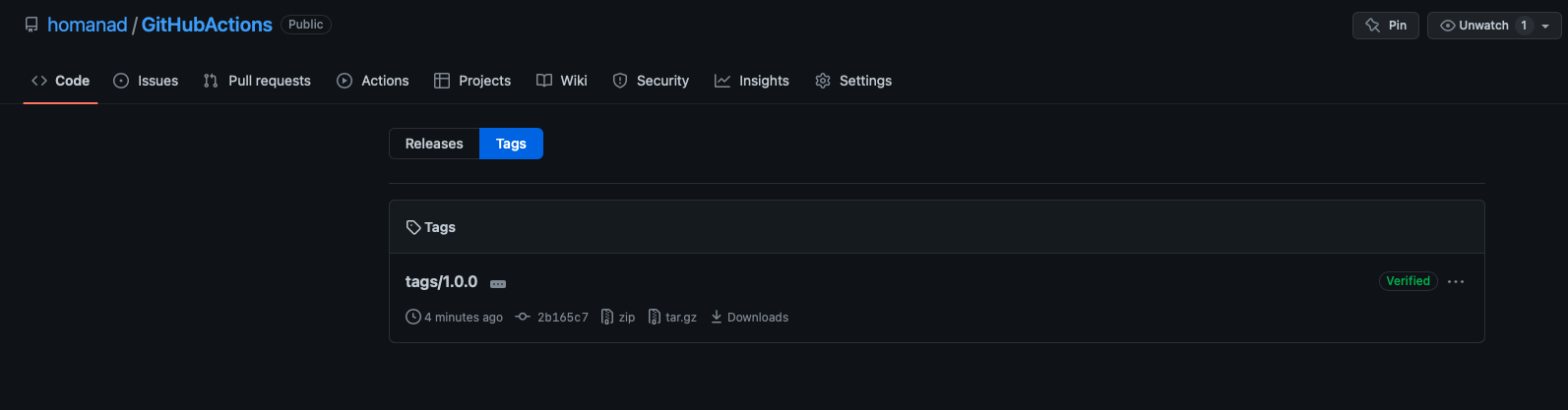
In short, with GitHub Actions you can do almost thing automatically. Because the GitHub Actions development community is very large, and the existing actions are also quite complete, try looking for something that you think for your project, or you can also create your own action (https://docs.github.com/en/actions/creating-actions).
Happy coding!

GitHub Actions for Android CI/CD

Channels & operators

StateFlow & SharedFlow